Data Engineer
Who is a data engineer? In the modern technological age, many organizations have realized that in many cases, tremendous value can be derived from the process of preparing data for investigation, and its results can serve as a growth engine for society.
With the increase in the use of Big Data technologies, organizations today are able to capture, store and analyze information in huge volumes, knowing that the data is the one that can answer the most pressing questions and have the highest financial value in any organization.
Data Engineer Should Work on the Questions Raised by Organizations
- What are the chances that a customer will buy a product?
- Which products will correctly recommend to a specific customer?
- How can I improve my website-based sales capabilities?
- Which products can be used as growth engines and which ones can be waived?
- What are the chances of certain mechanisms fail and cause losses?
It can be said that the technological challenges force organizations to access various technological solutions that meet organizational needs (often these are Open Source solutions). In order to establish, develop and manage information infrastructures that will be able to support the technological challenges, a new role was created that is Data Engineer. In this article, Coding compiler will answer the questions related to data engineer.
Skills Needed For a Data Engineer
- Who is a Data Engineer?
- What skills and capabilities are needed for Data Engineer?
When you look closely at the evolution of data creation and analysis, it is easy to understand that the subject becomes increasingly complex.
In the past, most of the information was generated in the organization, mainly by systems, and in most cases is stored in relational databases (RDBMS) based on the SQL language. Today, the information comes from many different sources that are often unrelated: IOT, sensors, log files from application sources And this information can represent, for example, billing, orders, history of deliveries, customer information, documentation of customer activity on the sales site, etc.
Organizations today are forced to deal with data that must be absorbed in a high rate, at high volumes, and these data can not necessarily be retained schematically ie relational database, and above all must be analyzed in real time or almost in real time.
If we try to simplify the technological environment for a moment in a typical technological organization, especially from the point of view of the data in the organization, there are many sources of information that flow into the organization’s data hub, some of which are defined as real-time events. Another type of data is the data at rest , which is the information that has been collected over time and which is required for improvement and preparation for analyses performed by the Data Scientist for example.
On the other hand, to the same information that flows into the organization there are several consumers who can be:
- Different apps with different APIs
- BI Investigation Tool (eg Tableau, Power BI )
- Analysts using SQL language
- Data Scientists

The Importance of Data Engineer
Data Engineer enables the organization to produce the required data from the data in an accessible and efficient manner. The Data Engineer is a core role in any modern organization and enables the organization or customers of the organization to begin work on analyzing the data effectively and to receive answers quickly and effectively to all those organizational questions with added value (functional/financial).
While organizations rely more and more on data intensively, the Data Engineer becomes increasingly important as a function of this – the demand for this role is increasing.
In a meta-graph taken from GoogleTrends, you can see that the concept and so on the role of Data Engineer has been on the rise for the last five years.

What is the role of the Data Engineer?
The role of the Data Engineer includes many different elements, but in order to summarize the areas of responsibility, the role of the data engineer can be defined as responsible for the reception, transmission and preparation of the data for analysis and advanced analysis in order to derive from the organizational information additional values translated to increase the profits of the organization Data to Value).
Otherwise, it is difficult for the organization to realize different capabilities. For example, real-time sales analysis, analysis of real-time fraud attempts, production of marketing messages to clients in real time, production of reports on the organization’s activities.
What’s more, Data Engineer’s main customer, the Data Scientist, will “waste” most of his time working on data rather than on drill models.
Data Engineer will be responsible for the organization’s information in its various stages, including the establishment, development, and maintenance of critical systems based on 24/7 data. The key areas for which Data Engineer is responsible can be divided into two parts:
1. Data Operations Tasks
- Choosing the most suitable technology for the Use Case
- Creation and development of infrastructure for the reception, transport, analysis and storage of data
- Creating mechanisms for full availability – High availability
- Maintaining the level of performance appropriate to the needs of the organization – Performance
- Automatic process development – Automation
2. Data Preparation
- Preparation of raw information for processing for data optimization – Staging
- Optimize the data to verify their integrity before using the app/reports
- Creation of testing processes for the reliability and integrity of the information
- Access of information to all organizational consumers (eg Application / Data scientists)
As you can understand, the Data Engineer will require system vision and the ability to identify and translate organizational needs into technologies and will be responsible for all the information flowing to the organization from the various sources. It will need to develop and maintain PipelineLines processes to migrate, process and manipulate data further, Efficiently collect and analyze information at extremely high rates and volumes (TBs) and using the most innovative technologies.
In addition, the Data Engineer is responsible for the information stored in the organization, which includes preparing the information for analysis.
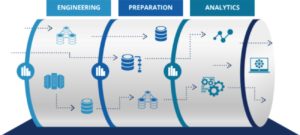
The Technological Fields The Data Engineer Deals With
So, as stated, Data Engineer is a challenging competitor that requires extensive knowledge in a number of technological fields.
In order to be able to provide solutions to a variety of technological challenges, he must have professional knowledge in many areas, including: infrastructure, virtualization, relational databases, NoSQL and Big Data technologies, application knowledge including programming control in one language or more, Machine Learning (so that he can speak the same language with one of his main clients, the Data Scientist ).
In the modern information age, when the frequency of buzz words as new technologies can often lead to confusion and even frustration, it is more important than ever to understand that in order to implement advanced elements such as Artificial Intelligence or Machine Learning, first of all knowledge is required in all data worlds to build an information infrastructure Such as: understand what the ETL process is, understand what a schematic and schematic information structure is, understand the most basic data language that is the SQL language.
Without this basic knowledge, for example, a data warehouse (DWH) may be constructed in a way that is not suitable for the type of activity. The organization and analytical results will differ on the same set of data or the results obtained will be delayed so that they will not be useful.
Data Engineer Technologies
The list below contains only part of the arsenal of knowledge and technologies that Data Engineer is required to recognize at Hands-On level:
- Knowledge of SQL language and database relational (RDBMS)
- Familiarity with the concept of DWH and ETL processes
- Practical experience of BigData / NoSQL environments
- Setting up and configuring data streaming mechanisms
- Setting up and configuring data pipelines
- Practical experience in Hadoop (Cloudera / Hortonworks)
- Practical experience with Ecosystem Hadoop (Hue / Hive / Impala / Oozie / Sqoop)
- Practical experience with Cloud Environments (AWS / Azure / Google Cloud)
- Practical Experience with Search Engines (Elastic Search / Solr)
- Data Cleansing
- Writing characterization and architecture documents
- Development in Python (or in different languages) and development on Spark
- Familiarity with the concept of Machine Learning
Make sure that Data Engineer is undoubtedly a senior and prestigious position at the Metacusa level, which reflects the high abilities of the experts in this position. All the best for your future and happy learning.

